Risk factors for deep vein thrombosis following total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures during winter
doi: 10.1515/fzm-2025-0017
-
Abstract:
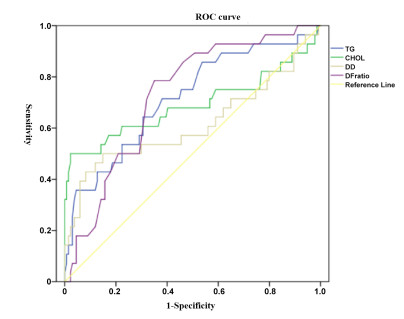
Objective To investigate the risk factors for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) following total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures during the winter. Methods A total of 162 patients who underwent total hip arthroplasty were categorized based on the development of DVT within 7 days postoperatively: 28 patients formed the DVT group and 134 patients the non-DVT group. Collected data included age, gender, history of glucocorticoid use, diabetes, hypertension, body mass index (BMI), triglyceride (TG) levels, cholesterol (CHOL) levels at admission, operative time, and postoperative bed rest duration. D-dimer (D-D) and fibrinogen (Fg) levels, along with the D-D/Fg ratio, were recorded on the first postoperative day. Group comparisons were performed using t-tests. Logistic regression analysis was conducted to identify independent risk factors, and the predictive value of these factors was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. Results In the DVT group, 18 patients had diabetes. Levels of TG (1.78 ± 0.44 mmol/L), CHOL (4.70 ± 1.84 mmol/L), D-D (0.40 ± 0.17 mg/L), and the D-D/Fg ratio (0.24 ± 0.07) were significantly higher than in the non-DVT group (P < 0.05). Logistic regression identified TG, CHOL, D-D, and the D-D/Fg ratio as independent risk factors for DVT, with odds ratios of 0.987, 2.395, 0.8, 4.992, and 9.004, respectively (P < 0.05). ROC curve analysis yielded areas under the curve (AUCs) of 0.715, 0.69, 0.614, and 0.726 for TG, CHOL, D-D, and the D-D/Fg ratio, respectively. Sensitivities were 0.643, 0.500, 0.429, and 0.857, and specificities were 0.694, 0.978, 0.918, and 0.537, respectively. Conclusion Elevated levels of TG, CHOL, D-D, and the D-D/Fg ratio are independent risk factors for DVT following total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients. Among these, the D-D/Fg ratio demonstrated the highest sensitivity and may serve as an effective marker for early-stage DVT screening. -
Key words:
- deep venous thrombosis /
- total hip replacement /
- senile patients /
- risk factor /
- winter
-
Table 1. Comparison of general data between two groups of patients
Influencing factors DVT (N = 28) Without DVT (N = 134) t/χ2 P Age 69.4± 7.9 71.0± 7.4 1.00 0.316 Gender Male 16 71 0.16 0.688 Female 12 63 Operation time (h) 1.62± 0.36 1.54± 0.38 1.02 0.312 Postoperative bed rest time (h) 25.3± 5.7 24.3± 6.6 2.00 0.842 Hormone use Yes 9 22 3.70 0.054 No 19 112 Diabetes Yes 18 56 4.72 0.030 No 10 78 Hypertension Yes 6 32 0.08 0.781 No 22 102 TG (mmol/L) 1.78± 0.44 1.49± 0.34 3.35 0.002 CHOL (mmol/L) 4.70± 1.84 3.63± 0.96 2.99 0.006 BMI 25.4± 4.6 24.3± 6.6 0.81 0.421 D-D (mg/L) 0.40± 0.17 0.33± 0.10 2.15 0.039 Fg (g/L) 1.84± 1.06 2.54± 2.23 1.63 0.106 D-D/Fg 0.24± 0.07 0.18± 0.09 3.68 < 0.001 DVT, deep vein thrombosis; TG, triglyceride; CHOL, cholesterol; BMI, body fat number; D-D, D-dimer; Fg, fibrinogen. Table 2. Screening of risk factors for postoperative DVT
Predictive indicators B S.E. Wald P OR 95%CI diabetes 0.987 0.547 3.258 0.071 2.683 0.919-7.834 TG 2.395 0.726 10.889 0.001 10.968 2.644-45.489 CHOL 0.800 0.213 14.103 0 2.226 1.466-3.381 D-D 4.992 2.111 5.593 0.018 147.232 2.351-9221.482 D-D/Fg 9.044 3.249 7.750 0.005 8465.607 14.534-4.93×106 TG, triglyceride; CHOL, cholesterol; D-D, D-dimer; Fg, fibrinogen. Table 3. Parameters of ROC curves of risk factors for DVT
Predictive indicators AUC S.E. P 95%CI Boundary value sensitivity Specificity degree TG 0.715 0.056 0 0.605-0.826 1.61 0.643 0.694 CHOL 0.690 0.071 0.002 0.550-0.829 5.32 0.500 0.978 D-D 0.614 0.071 0.058 0.474-0.754 0.47 0.429 0.918 D-D/Fg 0.726 0.048 0.000 0.633-0.820 0.185 0.857 0.537 TG, triglyceride; CHOL, cholesterol; D-D, D-dimer; Fg, fibrinogen. -
[1] Clynes M A, Harvey N C, Curtis E M, et al. The epidemiology of osteoporosis. Br Med Bull, 2020; 133(1): 105-117. doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldaa005 [2] Reid I R, Billington E O. Drug therapy for osteoporosis in older adults. Lancet, 2022; 399(10329): 1080-1092. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02646-5 [3] Feng J N, Zhang C G, Li BH, et al. Global burden of hip fracture: the global burden of disease study. Osteoporos Int, 2024; 35(1): 41-52. doi: 10.1007/s00198-023-06907-3 [4] Onizuka N, Quatman C. Global barriers to hip-fracture care. Lancet Healthy Longev, 2024; 5(8): e510-e511. doi: 10.1016/S2666-7568(24)00088-6 [5] Yonai Y, Masarwa S, Ben Natan M, et al. Seasonal patterns of hip fracture incidence and mortality rates across age groups of older adults in Israel. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg, 2024; 50(6): 3125-3131. doi: 10.1007/s00068-024-02569-w [6] Zhang X L, Zhang Q, Zhang X, et al. Effect of vitamin D3 supplementation in winter on physical performance of university students: a one-month randomized controlled trial. J Int Soc Sports Nutr, 2023; 20(1): 2258850. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2023.2258850 [7] Li C, Jiang X, Yue Q, et al. Relationship between meteorological variations, seasonal influenza, and hip fractures in the elderly: a modelling investigation using 22-year data. Sci Total Environ, 2023; 862: 160764. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160764 [8] CRISTAL Study Group, Sidhu V S, Kelly T L, et al. Effect of aspirin vs enoxaparin on symptomatic venous thromboembolism in patients undergoing hip or knee arthroplasty: the CRISTAL randomized trial. JAMA, 2022; 328(8): 719-727. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.13416 [9] Anderson D R, Doucette S, Kahn S R. Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis after hip or knee arthroplasty. N Engl J Med, 2018; 378(19): 1848-1849. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1803708 [10] Ambrose A F, Cruz L, Paul G. Falls and fractures: a systematic approach to screening and prevention. Maturitas, 2015; 82(1): 85-93. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2015.06.035 [11] Forster R, Stewart M. Anticoagulants (extended duration) for prevention of venous thromboembolism following total hip or knee replacement or hip fracture repair. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2016; 3(3): CD004179. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004179.pub2 [12] Matharu G S, Kunutsor S K, Judge A, et al. Clinical effectiveness and safety of aspirin for venous thromboembolism prophylaxis after total hip and knee replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. JAMA Intern Med, 2020; 180(3): 376-384. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.6108 [13] Aggarwal V A, Sambandam S, Wukich D. The impact of obesity on total hip arthroplasty outcomes: a retrospective matched cohort study. Cureus, 2022; 14(7): e27450. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27450 [14] Shimoyama Y, Sawai T, Tatsumi S, et al. Perioperative risk factors for deep vein thrombosis after total hip arthroplasty or total knee arthroplasty. J Clin Anesth, 2012; 24(7): 531-536. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2012.02.008 [15] Migliorini F, Maffulli N, Velaj E, et al. Antithrombotic prophylaxis following total hip arthroplasty: a level I Bayesian network meta-analysis. J Orthop Traumatol, 2024; 25(1): 1. doi: 10.1186/s10195-023-00742-2 [16] Azboy I, Barrack R, Thomas AM, et al. Aspirin and the prevention of venous thromboembolism following total joint arthroplasty: commonly asked questions. Bone Joint J, 2017; 99(11): 1420-1430. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.99B11.BJJ-2017-0337.R2 [17] Li Y, Shan J. Study on the correlation between high density lipoprotein and lower extremities deep venous thrombosis in patients undergoing hip arthroplasty. Phlebology, 2022; 37(7): 516-521. doi: 10.1177/02683555221090309 [18] Bartlett M, Mauck K F, Bierle D M, et al. Updates in venous thromboembolism management: evidence published in 2016. Hosp Pract, 2017; 45(3): 65-69. doi: 10.1080/21548331.2017.1341801 [19] Anderson D R, Dunbar M, Murnaghan J, et al. Aspirin or rivaroxaban for VTE prophylaxis after hip or knee arthroplasty. N Engl J Med, 2018; 378(8): 699-707. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1712746 [20] Heckmann N D, Piple A S, Wang J C, et al. Aspirin for venous thromboembolic prophylaxis following total hip and total knee arthroplasty: an analysis of safety and efficacy accounting for surgeon selection bias. J Arthroplasty, 2023; 38(7 Suppl 2): S412-S419. e1. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2023.02.066 [21] Jones C W, Spasojevic S, Goh G, et al. Wound discharge after pharmacological thromboprophylaxis in lower limb arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty, 2018; 33(1): 224-229. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2017.07.046 [22] Lim C, Roh Y H, Kim D W, et al. Is the may-thurner syndrome a major risk factor for deep vein thrombosis in total hip arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Surg, 2024; 16(1): 34-40. doi: 10.4055/cios23128 [23] Jones C W, Parsons R, Yates P J. Increased incidence of venous thromboembolism following hip or knee arthroplasty in winter. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong), 2020; 28(2): 2309499020920749. doi: 10.1177/2309499020920749 [24] Ogundeji S P, Fasola F A, Kotila T R. Hypertension and diabetes mellitus are associated with deep venous thromboembolism: a case control study. Ann Ib Postgrad Med, 30; 22(1): 34-38. [25] Lin Z, Sun H, Li D, et al. Thrombin antithrombin complex concentration as an early predictor of deep vein thrombosis after total hip arthroplasty and total knee arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2022; 23(1): 574. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05532-1 [26] Fang X, Shen Y, Wang M, et al. Predictive value of Caprini risk assessment model, D-dimer, and fibrinogen levels on lower extremity deep vein thrombosis in patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Front Neurol, 2024; 15: 1370029. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1370029 [27] Mlačo A, Mlačo N, Begić E, et al. D-Dimer and fibrinogen values according to the localization of deep venous thrombosis. Int J Angiol, 2023; 32(4): 243-247. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1759819 -


 投稿系统
投稿系统


 下载:
下载: